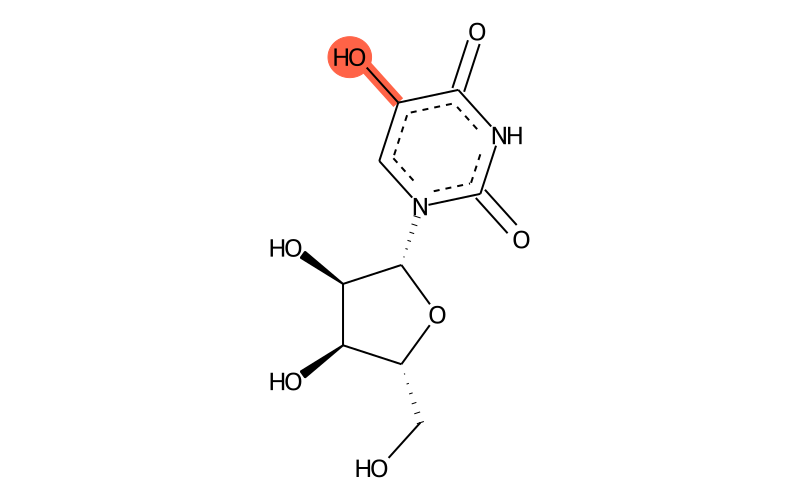
Summary
| Full name | 5-hydroxyuridine |
| IUPAC name | 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4-dione |
| Short name | ho5U |
| MODOMICS code new | 2000000050U |
| MODOMICS code | 50U |
| Synonyms |
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4-dione
1-((2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-5-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]-5-hydroxy-pyrimidine-2,4-dione 1-(beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-5-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 2,4(1H,3H)-Pyrimidinedione, 5-hydroxy-1-.beta.-D-ribofuranosyl- 36675-91-9 4,5-dihydroxy-1-pentofuranosylpyrimidin-2(1H)-one 5-Hydroxyuridine 5-Oxouridine 957-77-7 AC1L3RPQ C9-H12-N2-O7 C9H12N2O7 CHEBI:149645 CID94196 CJ-28906 CTK5H8174 DTXSID60914856 EINECS 213-487-1 Isobarbituric acid, 1-.beta.-D-ribofuranosyl- isobarbituridine MFCD00010571 NS00042468 NSC73376 SCHEMBL451947 Uridine, 5-hydroxy- Uridine,5-hydroxy- ZINC1707733 |
| Nature of the modified residue | Natural |
| RNAMods code | ∝ |
| Residue unique ID | 64 |
| Found in RNA | Yes |
| Related nucleotides | 360 |
| Enzymes |
TrhO (Escherichia coli) TrhP (Escherichia coli) |
| Found in phylogeny | Eubacteria |
Chemical information
| Sum formula | C9H12N2O7 |
| Type of moiety | nucleoside |
| Degeneracy | not applicable |
| ChEBI ID | 149645 |
| CAS Registry Number | 957-77-7 |
| SMILES | OC[C@@H]1[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]([n]2c(=O)[nH]c(=O)c(O)c2)O1 |
| logP | -3.1463 |
| TPSA | 145.01 |
| Number of atoms | 18 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Acceptors 1 (HBA1) | 7 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Acceptors 2 (HBA2) | 8 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Donors (HBD) | 5 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C9H12N2O7/c12-2-4-5(14)6(15)8(18-4)11-1-3(13)7(16)10-9(11)17/h1,4-6,8,12-15H,2H2,(H,10,16,17)/t4-,5-,6-,8-/m1/s1 |
| InChIKey | QXDXBKZJFLRLCM-UAKXSSHOSA-N |
| Search the molecule in external databases | ChEMBL PubChem Compound Database Ligand Expo WIPO |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SIDs |
10226361
10584950 14872330 44424827 57335752 79026352 85349202 104412091 129087852 135051756 163211718 179680397 223514260 226772454 249583326 252228281 252372025 252408491 254787918 256263376 274612578 304748877 319128775 329883573 341155480 342526813 346570895 349967039 354325081 355132463 374050309 375156824 375288008 377413000 378020730 384471996 385015367 386261273 387146318 388882042 404828870 415794046 434738072 439351830 439642373 443501166 |
* Chemical properties calculated with Open Babel - O'Boyle et al. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J Cheminform 3, 33 (2011) (link)
QM Data:
| Dipole Magnitude [D]: | 7.846732326 |
| Energy [Eh]: | -985.897780793918 |
| HOMO [eV]: | -8.7995 |
| LUMO [eV]: | 0.7715 |
| Gap [eV]: | 9.571 |
Download QM Data:
| Charges | charge.txt |
Download Structures
| 2D | .png .mol .mol2 .sdf .pdb .smi |
| 3D | .mol .mol2 .sdf .pdb |
Tautomers
| Tautomers SMILES |
OCC1C(O)C(O)C(N2C(=O)NC(=O)C(=O)C2)O1 tautomer #0
OCC1C(O)C(O)C(n2c(=O)[nH]c(=O)c(O)c2)O1 tautomer #1 OCC1C(O)C(O)C(N2C(O)=NC(=O)C(=O)C2)O1 tautomer #2 OCC1C(O)C(O)C(N2C(=O)N=C(O)C(=O)C2)O1 tautomer #3 OCC1C(O)C(O)C(n2c(O)nc(=O)c(O)c2)O1 tautomer #4 OCC1C(O)C(O)C(n2c(=O)nc(O)c(O)c2)O1 tautomer #5 |
| Tautomer image | Show Image |
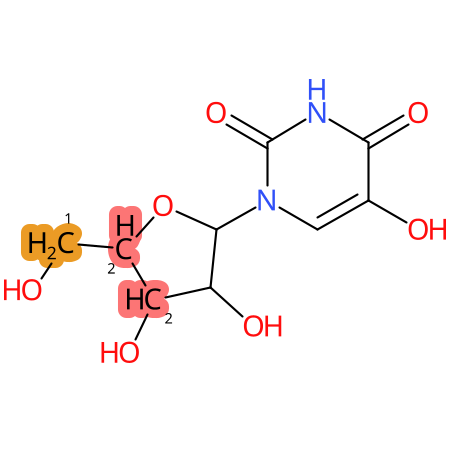
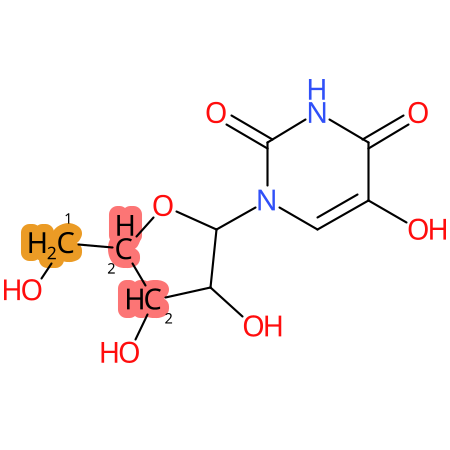
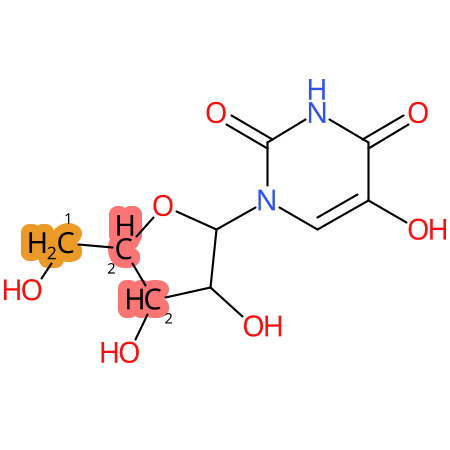
Predicted CYP Metabolic Sites
| CYP3A4 | CYP2D6 | CYP2C9 |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
* CYP Metabolic sites predicted with SMARTCyp. SMARTCyp is a method for prediction of which sites in a molecule that are most liable to metabolism by Cytochrome P450. It has been shown to be applicable to metabolism by the isoforms 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C19, 2E1, and 3A4 (CYP3A4), and specific models for the isoform 2C9 (CYP2C9) and isoform 2D6 (CYP2D6). CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP2C9 are the three of the most important enzymes in drug metabolism since they are involved in the metabolism of more than half of the drugs used today. The three top-ranked atoms are highlighted. See: SmartCYP and SmartCYP - background; Patrik Rydberg, David E. Gloriam, Lars Olsen, The SMARTCyp cytochrome P450 metabolism prediction server, Bioinformatics, Volume 26, Issue 23, 1 December 2010, Pages 2988–2989 (link)
LC-MS Information
| Monoisotopic mass | 260.0645 |
| Average mass | 260.201 |
| [M+H]+ | 261.0717 |
| Product ions | 129 |
| Normalized LC elution time * | not available |
| LC elution order/characteristics | not available |
* normalized to guanosine (G), measured with a RP C-18 column with acetonitrile/ammonium acetate as mobile phase.
Comments
ho5U at the wobble position of bacterial tRNA has been demonstrated in null-mutation CmoB. Null mutation of CmoA in S. enterica results in the accummulation of tRNA containing mo5U34 and ho5U34.
Chemical groups contained
| Type | Subtype |
|---|---|
| other | hydroxyl |
Reactions producing 5-hydroxyuridine
| Name |
|---|
| U:ho5U |
Reactions starting from 5-hydroxyuridine
| Name |
|---|
| ho5U:cmo5U |
| ho5U:mo5U |
Publications
| Title | Authors | Journal | Details | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The wobble hypothesis revisited: uridine-5-oxyacetic acid is critical for reading of G-ending codons. | Nasvall SJ, Chen P, Bjork GR | RNA | [details] | 17942742 | - |
| Isolation of 5-hydroxyuridine (iso-barbituridine) from yeast ribonucleic acids. | Lis AW, Passarge WE | Arch Biochem Biophys | [details] | 5957714 | - |
Last modification of this entry: Sept. 15, 2025