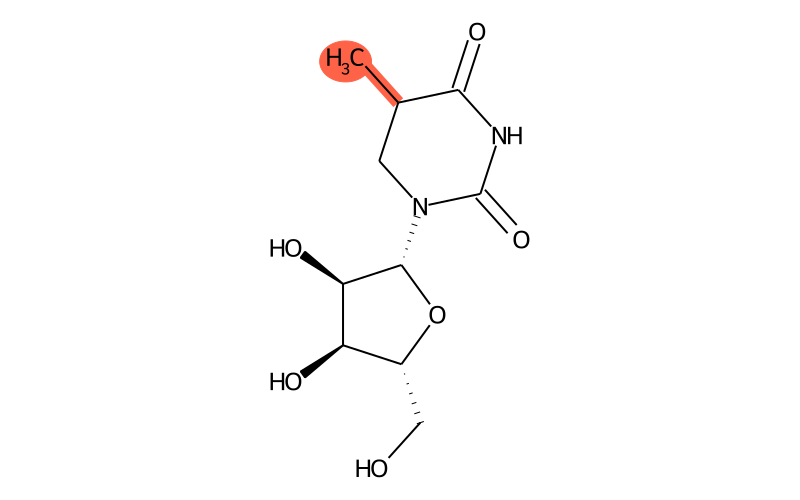
Summary
| Full name | 5-methyldihydrouridine |
| IUPAC name | 1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4-dione |
| Short name | m5D |
| MODOMICS code new | 2000000058U |
| MODOMICS code | 58U |
| Synonyms |
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methyl-1,3-diazinane-2,4-dione
1-((2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)-5-methyldihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 1463-10-1 23067-10-9 5,6-Dihydro-5-methyluridine 5-Methyl-5,6-dihydrouridine 5-methyldihydrouridine 5-Methyluridine CS-0114106 CTK4F0814 DIHYDRORIBOSYLTHYMINE DTXSID00617899 HY-130803 MFCD09842115 N/A Ribothymidine RTR-005799 SCHEMBL1964824 TR-005799 Uridine, 5,6-dihydro-5-methyl- Uridine, 5-methyl- |
| Nature of the modified residue | Natural |
| RNAMods code | ρ |
| Residue unique ID | 17 |
| Found in RNA | Yes |
| Related nucleotides | 364 |
Chemical information
| Sum formula | C10H16N2O6 |
| Type of moiety | nucleoside |
| Degeneracy | not applicable |
| SMILES | CC1C(=O)NC(=O)N([C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)C1 |
| logP | -2.12 |
| TPSA | 119.33 |
| Number of atoms | 18 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Acceptors 1 (HBA1) | 8 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Acceptors 2 (HBA2) | 8 |
| Number of Hydrogen Bond Donors (HBD) | 4 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C10H16N2O6/c1-4-2-12(10(17)11-8(4)16)9-7(15)6(14)5(3-13)18-9/h4-7,9,13-15H,2-3H2,1H3,(H,11,16,17)/t4?,5-,6-,7-,9-/m1/s1 |
| InChIKey | BTFXIEGOSDSOGN-KWCDMSRLSA-N |
| Search the molecule in external databases | ChEMBL PubChem Compound Database Ligand Expo WIPO |
| PubChem CID | |
| PubChem SIDs |
* Chemical properties calculated with Open Babel - O'Boyle et al. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J Cheminform 3, 33 (2011) (link)
QM Data:
| Dipole Magnitude [D]: | 5.321653152 |
| Energy [Eh]: | -951.251192220928 |
| HOMO [eV]: | -9.7697 |
| LUMO [eV]: | 1.5085 |
| Gap [eV]: | 11.2782 |
Download QM Data:
| Charges | charge.txt |
Download Structures
| 2D | .png .mol .mol2 .sdf .pdb .smi |
| 3D | .mol .mol2 .sdf .pdb |
Tautomers
| Tautomers SMILES |
CC1C(=O)NC(=O)N(C2C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)C1 tautomer #0
CC1=C(O)NC(=O)N(C2C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)C1 tautomer #1 CC1C(=O)N=C(O)N(C2C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)C1 tautomer #2 CC1C(O)=NC(=O)N(C2C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)C1 tautomer #3 CC1=C(O)N=C(O)N(C2C(O)C(O)C(CO)O2)C1 tautomer #4 |
| Tautomer image | Show Image |
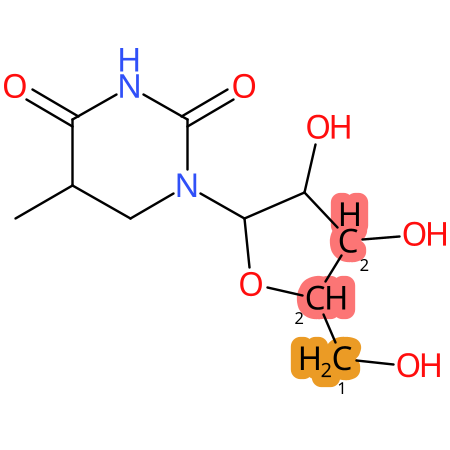
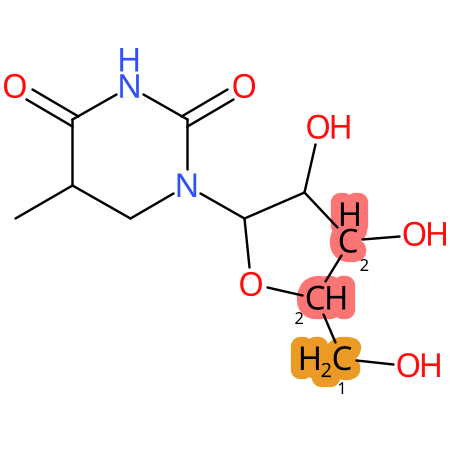
Predicted CYP Metabolic Sites
| CYP3A4 | CYP2D6 | CYP2C9 |
|---|---|---|
|

|
|
* CYP Metabolic sites predicted with SMARTCyp. SMARTCyp is a method for prediction of which sites in a molecule that are most liable to metabolism by Cytochrome P450. It has been shown to be applicable to metabolism by the isoforms 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C19, 2E1, and 3A4 (CYP3A4), and specific models for the isoform 2C9 (CYP2C9) and isoform 2D6 (CYP2D6). CYP3A4, CYP2D6, and CYP2C9 are the three of the most important enzymes in drug metabolism since they are involved in the metabolism of more than half of the drugs used today. The three top-ranked atoms are highlighted. See: SmartCYP and SmartCYP - background; Patrik Rydberg, David E. Gloriam, Lars Olsen, The SMARTCyp cytochrome P450 metabolism prediction server, Bioinformatics, Volume 26, Issue 23, 1 December 2010, Pages 2988–2989 (link)
LC-MS Information
| Monoisotopic mass | 260.1008 |
| Average mass | 260.244 |
| [M+H]+ | 261.1086 |
| Product ions | 129 |
| Normalized LC elution time * | not available |
| LC elution order/characteristics | not available |
* normalized to guanosine (G), measured with a RP C-18 column with acetonitrile/ammonium acetate as mobile phase.
Chemical groups contained
| Type | Subtype |
|---|---|
| methyl group | methyl at aliphatic C |
| ring modification | partial saturation |
Reactions producing 5-methyldihydrouridine
| Name |
|---|
| D:m5D |
Last modification of this entry: Sept. 15, 2025