DNAzymeBuilder is the first web server capable of automatic choice and assembly of RNA- and DNA-cleaving DNAzymes.
The following tutorial shows how to use DNAzymeBuilder's basic and advanced options to generate RNA- and DNA-cleaving DNAzymes.
Glossary
Binding arms: The right and left arms of a DNAzyme are designed based on the complement and reverse of the substrate region that are bound to the DNAzyme.
Catalytic core: Any DNAzyme has a unique catalytic core that has been identified by in vitro selection or by in vitro evolution.
Cleavage site: A cleavage site denotes the exact nucleotide position of the phosphodiester cleaved bond(s) within the substrate.
Cofactors: Cofactors are directly involved in catalysis or are required for the formation of the 3D structure that is ultimately compatible with catalysis.
Context: The context refers to the nucleotides upstream and downstream from the RS that have the potential to affect the catalytic activity of the DNAzyme.
DNAzyme: DNAzymes, also called deoxyribozymes and catalytic DNA, are nucleic acid enzymes that are capable of performing specific chemical reactions.
DNA-catalyzed hydrolytic cleavage: After the phosphodiester bond is cleaved, the hydrolytic cleavage of nucleic acids yields a left product with a 3’-hydroxyl terminus and a right product with a 5’-phosphate terminus.
DNA-catalyzed oxidative cleavage: Oxidative cleavage occurs when DNA is exposed to oxidative stress or other stresses, leading to the formation of excess compounds and DNA waste. Oxidative cleavage can occur at the base or sugar in a nucleotide.
Melting temperature: Tm is calculated using the Nearest neighbor (NN) equation and the thermodynamic tables described by SantaLucia et al. (1996).
Reaction: Reaction refers to the type of reaction performed by the DNAzyme.
Reaction pH: Reaction pH denotes the pH of the buffer utilized during in vitro selection.
Reaction rate: Reaction rate shows cleavage rates for different DNAzymes or different associated contexts of DNAzymes.
Recognition site: A recognition site, specific for any DNAzyme, denotes the sequence encompassing the cleavage site on the substrate.
Reaction temperature: Reaction temperature is the temperature at which the given DNAzyme carries out the cleavage reaction.
Right and left products: Right and left products are the DNAzyme cleavage products, and are determined by the exact position of the cleavage site and the type of cleavage reaction.
RRk: Relative Reported kobs
RRY(specific time): Relative Reported Yield at the specified time
RCY(specific time): Relative Calculated Yield at the specified time
Substrate: DNA or RNA sequence to be cleaved (provided by the user)
3’ and 5’ functional groups: 3’ and 5’ functional groups refer to functional groups at the 3’ and 5’ ends of the left and right products, respectively.
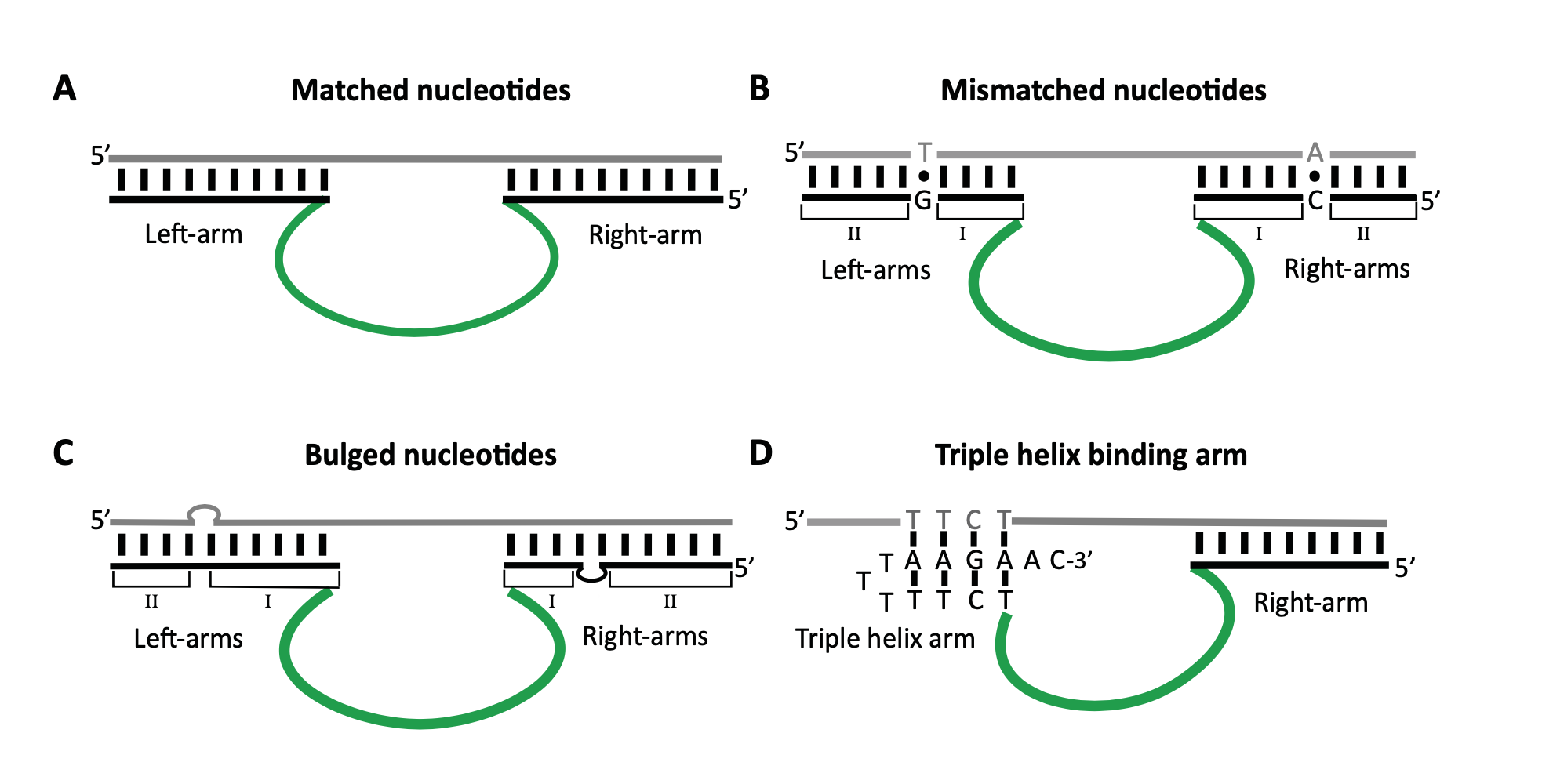
Nucleotide interactions
Occasionally, the presence of unpaired, mismatched and bulged nucleotides in the DNAzymes' binding arms improves the catalytic activity of these DNAzymes. In such cases, the DNAzymes’ arms are assembled taking the unpaired, mismatched, and/or bulged nucleotides into account so that the catalytic activity is optimal. Further details accompanying this explanation can be found in the following figure. RNA- and DNA-cleaving DNAzymes.
Results pages
DNAzymeBuilder results page shows a list of candidate DNAzymes to carry out the cleavage reaction on the query sequence. This page displays for each DNAzyme, it's name, sequence, cofactors, kobs, and the binding arms Tm. By clicking on a DNAzyme you'll be redirected to the single result page, which includes:
1. DNAzyme sequence: This is the assembled DNAzyme sequence. This sequence includes the right and left arms as well as the DNAzyme’s catalytic core.
2. Binding substrate: DNAzymeBuilder highlights the part of the substrate that binds to the DNAzyme.
3. Right and left products: DNAzymeBuilder reports cleavage products. If the query sequence is long, the products are presented only for the DNAzyme-binding regions and the remainder of the sequence is indicated by an ellipsis.
4. 3’ and 5’ functional groups: DNAzymeBuilder reports the functional groups at 3’ and 5’ ends of the left and right reaction products, respectively.
5. Optimized lengths of the binding arms: If optimal right and left arms lengths have been reported in the literature, DNAzymeBuilder will report such values. For the design of DNAzymes such lengths are used, however, if no such information is available, the algorithm assumes an optimal binding-arm length of 10 nucleotides.
6. Tm for binding arms: DNAzymeBuilder calculates the melting temperature of the left and right arms using the nearest neighbor (NN) model and the thermodynamic tables described by SantaLucia et. al. (1996). The Tm-calculation algorithm of DNAzymeBuilder is based on the Tm algorithm of Biopython.
7. Cofactors: DNAzymeBuilder eports the DNAzyme’s cofactor requirements for catalysis. When no cofactor dependency was reported, the phrase NR (Not Reported) is displayed in the notes section of the results page.
8.
Reaction rate and yield:
Cleavage rates vary for different DNAzymes and reaction conditions. For each DNAzyme-substrate pair, DNAzymeBuilder reports kinetics parameters depending on which of the following situations applies:
| RRYtime=Ymutant, modified core, the specific context/Yoriginal core, and context | (1) |
| RRkobs =kobs mutant, modified core, the specific context/kobs original core, and context | (2) |
| RCYtime = calculated Ymutant, modified core, the specific context/calculated Yoriginal core, and context | (3) |
9. Reaction pH: DNAzymeBuilder reports the pH of the buffer employed during in vitro selection. If additional biochemical characterization characterization of a DNAzyme has been carried out, and a different pH from that of the in vitro selection experiment is known to give better results, then, the latter is reported instead.
10. Reaction temperature: The reaction temperatures reported by DNAzymeBuilder have been extracted from the literature.
11. Note: DNAzymeBuilder notes are a summary of what was considered for the automatic choice and assembly of the DNAzyme, they also provide a report on the performance of the DNAzyme under specific conditions that may be of interest to the user.
12. Reference(s): DNAzymeBuilder provides the main reference along with associated publications, providing the following information for each publication: first author, year of publication, journal title, publication title, abstract, PubMed ID and DOI, as well as the reaction for which the DNAzyme was selected.
Browser compatibility
We tested DNAzymeBuilder webserver on the following systems/browsers
| OS | Chrome | Firefox | Microsoft Edge | Safari |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linux Ubuntu 20.04 LTS | not tested | 78.13.0esr | n/a | n/a |
| Windows 10 | 95.0.4638.69 | 94.0.1 | 95.0.1020.44 | not tested |
| Mac OSX | 95.0.4638.69 | 94.0.1 | not tested | 15.0 |
| Android 11 | 95.0.4638.74 | 94.0.12 | 95.0.1020.42 | n/a |