Introduction
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) were found to
be involved in many cellular processes from the gene
transcriptional regulation to the catalysis of chemical
reactions. Many ncRNAs, including cis-regulatory elements,
are modular biomolecules, composed largely of recurrent structural
motifs glued together via mutual interactions
into a compact, functional, 3D structure.
RNA Bricks database provides information about the recurrent RNA motifs and their interactions,
both with themselves and with proteins. In contrast to other similar tools
(RNA 3D Motif Atlas, RNA Frabase, Rloom) here RNA motifs are presented in
their natural environment, that is neighborhood of other molecules in a solution or in a crystal.
RNA Brick, what is that?
"RNA brick" is a set of interacting nucleotide residues from the same chain, flanked by WC or wobble base pairs. In particular we distinguish three types of RNA bricks or motifs. Stems are arrays of WC/wobble base pair tandems. Loops are motifs composed of single-stranded fragments flanked by WC/wobble pairs. Terminal fragments, or strands are single-stranded fragments with only one end involved in a WC/wobble pair.
How does it work?
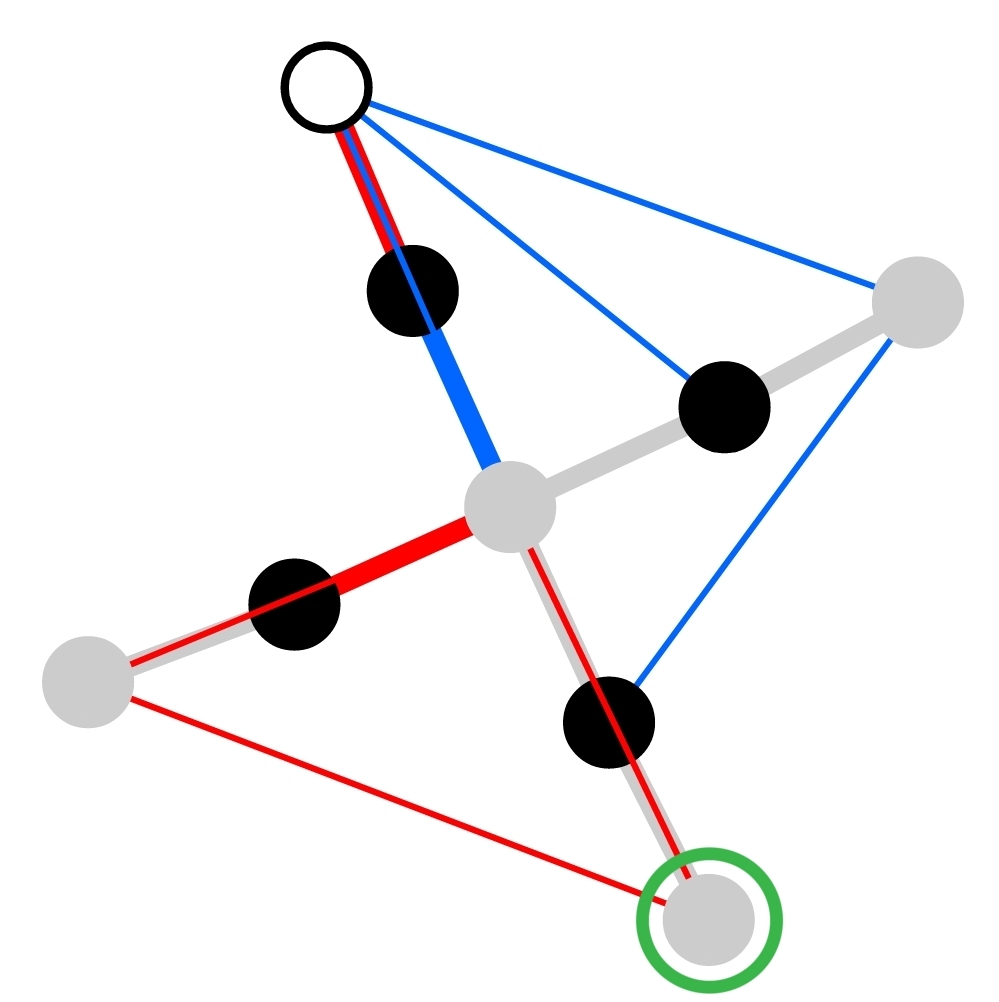
The RNA structures stored in this database are coded in a form of graphs.
Basic secondary structure motifs are represented as nodes. Black, grey and open circles
denote stems, loops, and single stranded motifs respectively. If an RNA motif is in
contact with a protein, corresponding node will be marked with a green circle.
The edges represent either bases shared by neighbor motifs (thick, grey lines), or tertiary
contacts (thin red or blue lines). Red edges depict intramolecular contacts, blue
crystallographic ones.
If two motifs are both neighbors, and in tertiary or crystallographic contact,
corresponding nodes will be linked with a thick edge of an appropriate color (red, or blue).
Please note that in RNA Bricks all contacts are treated equally. In particular a graph edge may represnt a signle h-bond, stacking, annotated basepair, or any combination of these contact types.
The graphs representing RNA structures are interactve and may be freely zoomed and moved. This feature is particularly useful in case of large RNA molecules with complex intercation networks (e.g. ribosomes)
Browsing structures
All listed entries can be browsed page by page, searched by keywords or filtered by Rfam/Uniprot IDs. Cliking on a molecular image or PDB ID in the left column (1) will display details of the given structure. Quality scores (2) represent an average reliability of a given structure RNA content. See Quality scores section for details.

Browsing motifs
One can select RNA motifs clicking directly on the graph (3) or selecting row in a table (1). Selected motifs may be visualized in Jmol by clicking on the "show in jmol" link (2).
 The interactive table is composed of the following columns:
The interactive table is composed of the following columns:
Secondary strcuture
Secondary strucutre graphs are based on MC-Annotate analysis. Nucleotides with green halos are in contact with a protein.
Fragment residues
This column lists residues from continuous chain segments forming a given motif. You can query for motifs with "chain id/residue id"
download - get a motif coordinates, sequence, list of h-bonds, and annotated base-pairs
search - use a motif as a RNA Bricks search query (structure, or sequence based)
Similar motifs
This column lists number of similar motifs at 1.0Å backbone RMSD. Click on a link to switch to the cluster view.
Contacts
This column lists motif neighbors (grouped by type). If a given motif forms annotated contacts with other RNA motifs, their names will be listed explicitly (4). You can click on these to see 2D diagram of an intercation.
Quality
Quality scores calculated for separate motifs. See Quality scores section for details.
Browsing clusters
Jmol applet on the right side of the clustrer view displays superposition of motifs selected in a table (1). Columns (2) and (3) list links to PDB structures containig selected motifs, and detailed information about a motif environment.

Selected motifs can be downloaded with link (5). A snapshot of current Jmol view can be taken with link (6). Quality scores listed in column (4) depict reliability of separate motifs. See Quality scores section for details.
Quality scores
RNA Bricks provide the following quality validation scores
clashes - a number of bad non-H-bond overlaps (0.4 Å or greater) per 1000 atoms. This score was determined with the Probe program from Molprobity suite.
geometry - a fraction of nucleotides with suspicious backbone torsion angles, that is not within a set of 54 favorable RNA backbone conformer defined by the RNA Ontology Consortium. This score was determined with the use of Suitename program from Molprobity suite.
e-density - a fraction of nucleotides with poor electron density. This score was derived from experimental structure factors deposited in PDB. Poor electron density means either weak signal (below 1 σ on average) or real-space correlation coefficients value below 0.7
All the above described scores are available on three scales
structure reliability - these scores reflect an average reliability of an RNA content of a given PDB structure
motif reliability - these scores are calculated for separate motifs and represent their average reliability
nucleotide reliability - this is a most detailed quality information available. In the Jmol view atoms forming bad clashes, nucleotides with suspicious backbone geometry or weak electron density can be marked with black halos.
Viewing RNA 3D motifs with Jmol
Selected motifs are dislayed in warm colors (red, orange, yelow, brown etc.). The Jmol applet provides followoing visualization options:
Display RNA - display motifs that are in contact with selected motifs within Asymmetric Unit (colorcode: grey)
Display RNA (symm) - display motifs that form crystallographic contacts with selected motifs (colorcode: blue)
Display protein - display trace of protein chains that are in contact with selected motifs. The protein chains that form crystallographic conatcts are transparent (colorcode: green)
Display complete RNA - display phosphate atoms trace of a whole RNA chains related to the selected motifs (colorcode; grey)
Display others - display selected motifs neighbors that are neither water/ion, nor protein
Display contacts - display h-bonds and residues that are in contact with selected motifs
Show hydrogens - display hydrogen atoms. These were added with Reduce program if not present in the original file.
Quality scores - mark residues with poor quality scores (see Quality scores section for details)
Searching by structure

To make exploration of RNA Bricks easier we enabled querying of the database with user-provided RNA structures. The search algorithm covers backbone coordinates of the input RNA using a representative subset of 3D motifs from the database. The coverings are based solely on coordinates of backbone atoms, no sequence or 2D structure information is used.
Preparing a query
The input-structure coordinates must be in PDB format (text or file) and each nucleotide should contain a seed atom. Currently the input size is limited to 40 nucleotides.
Modified ribonucleotides in input structure are treated as lone phosphates (if present). All non-nucleic acid residues e.g. protein chains, are neglected.
You can also specify PDB id and residue numbers of a query e.g.
0/312:317,0/319
Available search modes
- motifs in query
- This mode is used for finding best match of RNA 3D motifs within user provided structure.
- query in motifs
- In this mode best matches of the user-provided structure are found within RNA 3D motifs from the database.
Advanced options
There are two parameters for fine tuning the search algorithm
- Seed atom
- Here you can select a backbone atom that will be used to determine trial matches that are further refined based on all backbone atoms RMSD. Therefore if a residue miss atom you selected it will be discarded by the algorithm.
- Include motifs milieu
- Include neighboring nucleotides to the selected motfs. This option may be useful in combination with the query in motif mode.
- Selected PDB
- Use for search motifs derived from a selected PDB structure.
- Non-redundant RNA Structures
- Use RNA motifs derived from the Non-redundant RNA Structures Dataset. Note that this and the Select PDB cannot be used simultaneously.
- Eps
- This value is used for initial filtering of motifs. Small values of this parameter (below 1.0) result in a small number of trial motifs (and small sensitivity). Large values (over 5.0) will disable initial filtering, at the expense of the computation time. In most cases default value should provide best results
- Max rmsd
- This is a cut off value for selecting both initial (C3′-based) and final matches. In rare cases larger values of this parameter may increase the algorithm sensitivity.
Searching by sequence
The database provides a simple interface for making sequence-based queries. The queries relate to the complete motifs in the database and may be composed of any number of strands definifing a motif.
Any RNA motif is composed of a set of strands, with defined lengths and sequences
Preparing a query
The queries must be in FASTA format, with sequences representing consequtive segments of an RNA motif in standard four-letter code (A,G,U,C). The search algorithm accounts for cyclic permutations in the segments order.
-
single segment with a given sequence
>segment1
AAGUAG -
single segment of length 6 starting with 'A' and ending with 'G'
>segment1
A....G -
single segment composed of 6 purines.
>segment1
[AG]{6} -
a motif (stem or loop) composed of two segments; first with a given sequence, second with any length and sequence:
>segment1
AAGUAG
>segment2
.* -
a loop composed of two segments of length 5 and 12 (any sequence)
>segment1
.{5}
>segment2
.{12}
Case-sensitive search
Case sensitive option enables searching for modified residues. By default the sequence-based search algorithm is case-insensitive.
Aggregating results
References
If you find this tool useful please cite:
Chojnowski G, Waleń T, and Bujnicki JM
RNA Bricks—a database of RNA 3D motifs and their interactions
Nucleic Acids Research, 2013, 1–9 doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1084 [Epub 2013 Nov 13]
[pdf]
RNA 2D structures were annotated using ClaRNA:
Waleń T, Chojnowski G, Gierski P, and Bujnicki JM
ClaRNA: a classifier of contacts in RNA 3D structures based on
a comparative analysis of various classification schemes.
Nucl. Acids Res. (2014) 42 (19): e151 doi: 10.1093/nar/gku765
[pdf]
Tutorials
Working with the RNA Bricks interface
In this tutorial you will learn how to use the RNA Bricks web interface.
Quality scores in RNA Bricks
This tutorial presents the structure quality scores available in RNA Bricks.
Basic usage of the 3D search engine
RNA Bricks database provides a simple clustering method that groups
RNA motifs with the same secondary structure and number of ribonucleotide residues.
Therefore in some cases two motifs that have similar tertiary structures are classified
to separate clusters due to differences in secondary structure annotation and/or presence
of variable loops.
With this tutorial you will learn how to to query the database for all RNA 3D motifs that
share common substructures with a motif of interest.
Advandced usage of the 3D search engine
This tutorial shows how to build advanced RNA Bricks 3D search engine queries. In particular you will learn how to search for RNA 3D motifs that share common substructure.
